What Are Carbohydrates and Why Do They Matter in Diabetes?
What Are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates (also called "carbs") are one of the three main types of food your body needs. Think of them as fuel for your body. Just like a car needs gasoline to run, your body needs carbohydrates to have energy so you can think, walk, and do everything you do each day.
There are three main types of food that provide us with calories- they are called macronutrients and they are:
Carbohydrates - give quick energy
Proteins - help build and repair the body
Fats - give long-lasting energy
How Do Carbohydrates Work in Your Body?
When you eat carbohydrates, your body converts them into glucose (a type of sugar). Glucose travels through your blood and gives energy to every cell in your body.
Imagine that glucose is like energy packages that travel along your body's "highways" (your blood) to deliver energy where it's needed.
What Happens If You Eat Too Many Carbohydrates?
If you eat more carbohydrates than your body needs at that moment:
Your body stores the extra sugar in your liver and muscles (like a pantry)
If that "pantry" fills up, your body converts the sugar into fat to use later
Why Are Carbohydrates Important If I Have Diabetes?
If you have diabetes or prediabetes, carbohydrates make your blood sugar go up. The more carbohydrates you eat at one time, the higher your glucose will rise.
Important Point: This does NOT mean you should eliminate carbohydrates completely. Your brain and other parts of your body need them to function well.
What You DO Need to Do:
✅ Control portions - Don't eat too much at once
✅ Choose healthier carbohydrates - Ones that have fiber
✅ Spread them throughout the day - Don't eat a lot in just one meal
Where Are Carbohydrates Found?
Carbohydrates are in many foods:
🌾 Grains and Cereals
Bread, rice, pasta
Oatmeal, tortillas, cereals
🍎 Fruits
Apples, bananas, strawberries
Oranges, mangoes, grapes
🥔 Starchy Vegetables
Potatoes, corn
Peas, plantains
🫘 Legumes
Beans, lentils
Chickpeas, peas
🥛 Dairy Products
Milk, yogurt
(Cheese has very few carbohydrates)
🍪 Sweets and Snacks
Cookies, sodas
Ice cream, pastries, cakes
Types of Carbohydrates: Simple vs. Complex
Not all carbohydrates affect your body the same way. Think of this as fast fuel vs. slow fuel.
Simple Carbohydrates (Fast Fuel)
What are they? Sugars that the body digests very quickly
What do they do? Make your sugar rise fast (like a rocket 🚀)
Examples:
White sugar
Sodas and juices
White bread
Candy and sweets
Cakes and pastries
Complex Carbohydrates (Slow Fuel)
What are they? Carbohydrates with lots of fiber that take longer for the body to digest
What do they do? Make your sugar rise slowly (like going up a gentle ramp 📈)
Examples:
Whole grain bread (100% whole grain)
Oatmeal
Brown rice
Beans and lentils
Vegetables (especially with skin)
Key Tip
Choose more complex carbohydrates and fewer simple carbohydrates to avoid your sugar going up and down sharply. This will help you feel better and have more energy throughout the day.
How to Manage Carbohydrates With Diabetes
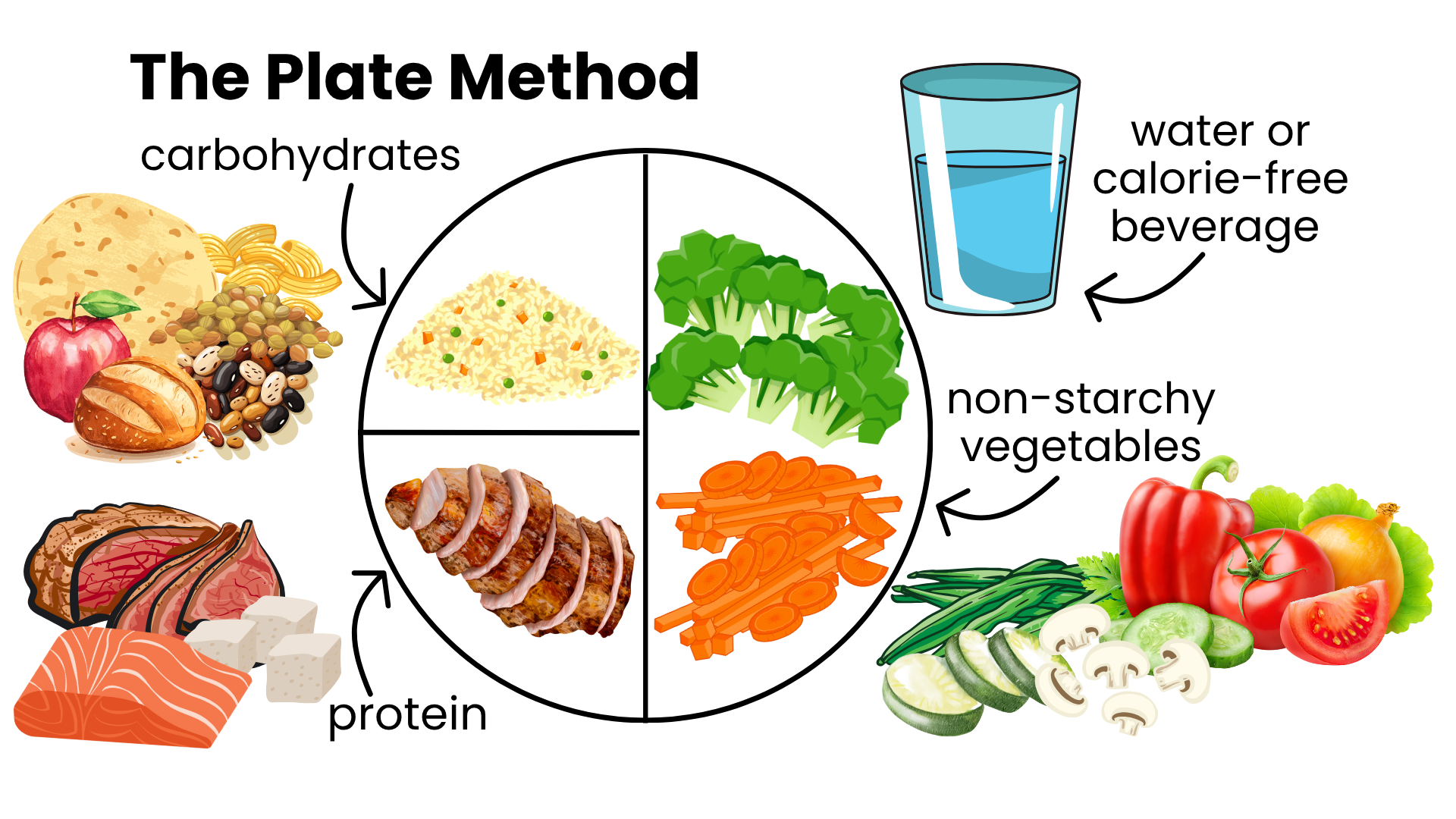
1️⃣ The Plate Method (The Easiest Way!)
The Plate Method is like putting together a simple puzzle on your plate. You don't need to weigh or measure anything.
Use a 9-inch (23 cm) plate and divide your plate like this:
½ of the plate 🥦 = Non-starchy vegetables
Lettuce, broccoli, spinach
Tomatoes, cucumbers, carrots
Cauliflower, peppers, green beans
¼ of the plate 🍗 = Lean protein
Chicken, fish, turkey
Eggs, tofu
Lean beef or pork
¼ of the plate 🍚 = Carbohydrates
Brown rice, pasta
Potatoes, corn, beans
Fruits, tortillas
Add a glass of water or a sugar-free or calorie-free beverage 💧
Simple Visual Guide
One serving of carbohydrates should be the size of your closed fist or the size of a tennis ball. This is approximately 1 cup or about 30 grams of carbohydrates.
2️⃣ Carbohydrate Counting (For Those Using Insulin)
If you use mealtime insulin (especially if you have type 1 diabetes), counting carbohydrates helps you know how much insulin you need.
How to Read a Food Label
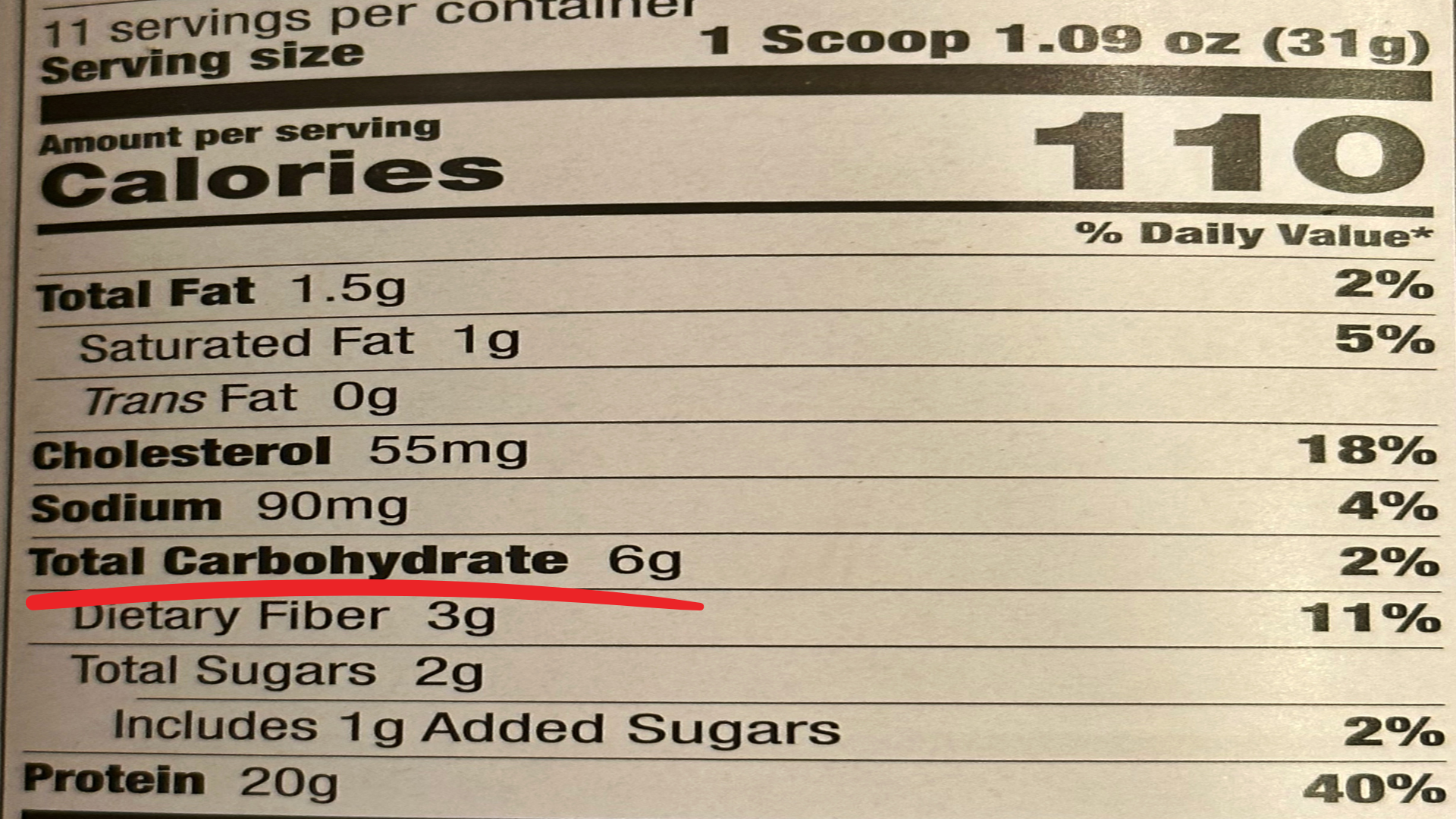
Step 1: Look for the Serving Size
Everything on the label is based on this amount
Example: 1 scoop
Step 2: Find "Total Carbohydrate"
This number includes: sugars + fiber + starches
Example: 6 grams
Step 3: Do the Math
If you eat more than one serving, multiply
Example: If you eat 3 scoops and each 1 scoop has 6 grams
Calculation: 3 scoops x 6 grams = 18 grams of total carbohydrates
⚠️ DON'T Confuse
Total Carbohydrate = What you should count
Sugars = Just part of the total (already included in the total)
3️⃣ How Many Carbohydrates Should I Eat?
The right amount depends on:
Your age
Your physical activity level
Your medications
Your health goals
🩺 Your doctor or dietitian can help you personalize this amount.
General Guide per the American Diabetes Association (Reference Only)
Per meal:
Women: 45-60 grams
Men: 60-75 grams
Example of 45-60g of carbohydrates:
1 cup of brown rice (45g)
or 1 medium tortilla (15g) + 1 medium apple (25g) + ½ cup beans (20g) = 60g total
or 1 cup whole grain pasta (45g) + green salad (0-5g)
Important Rule
Spread carbohydrates throughout the day. Don't "save" all your carbohydrates to eat them all at once. This prevents big sugar spikes.
❌ DON'T do this: Eat very little at breakfast and lunch, then eat lots of carbs at dinner
✅ DO this: Eat a moderate amount of carbohydrates at each meal
Steps to Get Started (From Easiest to Most Advanced)
🥉 Level 1: Beginner
Identify the carbohydrates on your plate
Learn which foods have carbohydrates
Start noticing how much you eat at each meal
You don't need to count anything yet
🥈 Level 2: Intermediate
Use the Plate Method
Divide your plate into the three sections
Use your fist as a guide for portions
Drink water instead of sodas or juices
🥇 Level 3: Advanced
Learn to count carbohydrates
Read food labels at home
Practice measuring portions with measuring cups
This makes eating out easier
💡 Tip: You don't need to move to the next level right away. Take your time and master each step.
Extra Tips for Success
💧 Drink Water
Water is the best drink because it has no calories or carbohydrates. Avoid sugar-sweetened beverages like:
Sodas
Juices (even "natural" ones)
Sweetened drinks
Sports drinks
If you want flavor: Try water with slices of lemon, cucumber, or berries.
🌾 Choose More Fiber
Look for foods with at least 3-5 grams of fiber per serving. Fiber helps:
Sugar rise more slowly
You feel full longer
Improve your digestion
High-fiber foods:
Beans and lentils
Vegetables (especially with skin)
Fruits with skin (apples, pears)
Whole grains (oatmeal, brown rice)
Quick Summary - The Most Important Points
✅ Carbohydrates give energy to your body, especially your brain
✅ They raise blood sugar, which is why you need to be careful if you have diabetes
✅ Don't eliminate carbohydrates, just control:
How much you eat (portions)
What type you eat (prefer complex with fiber)
When you eat them (spread throughout the day)
✅ The Plate Method is the easiest way to start
✅ Drink water instead of sweetened beverages
✅ Work with your medical team to create a personalized plan
Ready to Take the First Step?
Remember: You don't have to do everything perfectly from the start. Every small change counts and gets you closer to your health goals.
Start Today With One of These Actions:
Identify the carbohydrates in your next meal
Try the Plate Method at dinner
Switch one soda for water
Read a food label you have at home
Talk to your doctor about your carbohydrate goals
Share This Information
Did this guide help you? Share it with someone who's also learning to manage their diabetes or prediabetes. Together you can support each other on this journey.
💬 Have questions or want to suggest future topics? Leave your comments below or send us questions here.
Learn, understand, and live better with diabetes.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes and is not intended as a substitute for medical care from your healthcare team. Always talk to your doctor or healthcare team before making major changes to your diet or exercise routine.